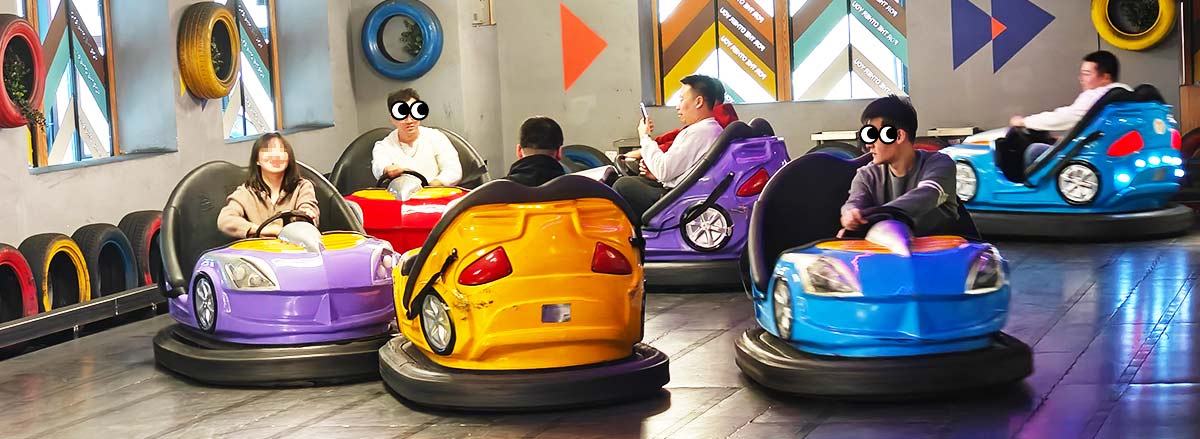

When you think of amusement parks, one ride stands out above all others: bumper cars. Known for their fun and unpredictable nature, these electrifying vehicles are the heart of any fairground or theme park. But did you know that bumper cars history is rich and fascinating, with these rides evolving significantly since their creation? Let's dive into the history, mechanics, and modern-day innovations that make dodgems (as they're called in the UK) a timeless favorite.
Amusement Park Bumper cars, also known as dodgems, have been thrilling families and thrill-seekers for almost a century. Their origins trace back to the Stoehrer brothers, Max and Harold, who first patented the idea in December 1920, launching the Dodgem brand. While many credit the Stoehrer brothers for the invention, there is some debate over whether Victor Levand, a General Electric worker, contributed to the technology that led to the bumper car's creation. However, what’s clear is that the Dodgem Company was the first to manufacture bumper cars, and their models were the first commercially successful ones.
The early models were far from perfect. Constructed from tin, the first dodgem cars often required repairs after every ride. They were prone to damage, with parts often falling off, making them a nightmare to operate. Yet, despite their flaws, they captured the imagination of the public. The thrill wasn’t just in driving the cars, but in the idea of safely crashing into other vehicles without harm.
Early bumper car designs didn’t prioritize durability or safety, but rather the concept of driving and dodging other cars. Hence, the term dodgems—meaning "to dodge"—was born. The ride became so popular that its popularity couldn’t be stopped, and improvements were made to address safety and reliability issues.
Have you ever wondered how these small, electric cars manage to move around without rails or tracks? Bumper cars are powered through a combination of electricity and mechanical engineering. Here's how they work:
Electric Circuit: Most dodgem cars use a conductive floor and ceiling system. The cars are connected to a metal pole that reaches up to a ceiling grid, allowing an electric current to pass through, powering the car.
Steering Mechanism: The early dodgems were known for their poor steering, which made for even more chaotic and fun collisions. Modern bumper cars have much better steering systems for more control.
Collision Absorption: To reduce the impact of crashes, bumper cars are equipped with rubber bumpers, which absorb the shock from collisions and ensure the safety of the riders.
Power Source: In the beginning, bumper cars used an overhead power system where electricity was delivered from above. Today, many modern bumper cars use battery-powered systems for greater flexibility and reduced environmental impact.
Over the years, dodgems have gone through significant improvements. By the 1930s, competitors like the Lusse Brothers entered the market with their own models, which boasted improved steering and design. They introduced the Auto-Skooter, a more refined version that was better at controlling steering and had fewer mechanical issues than the early Dodgem cars.
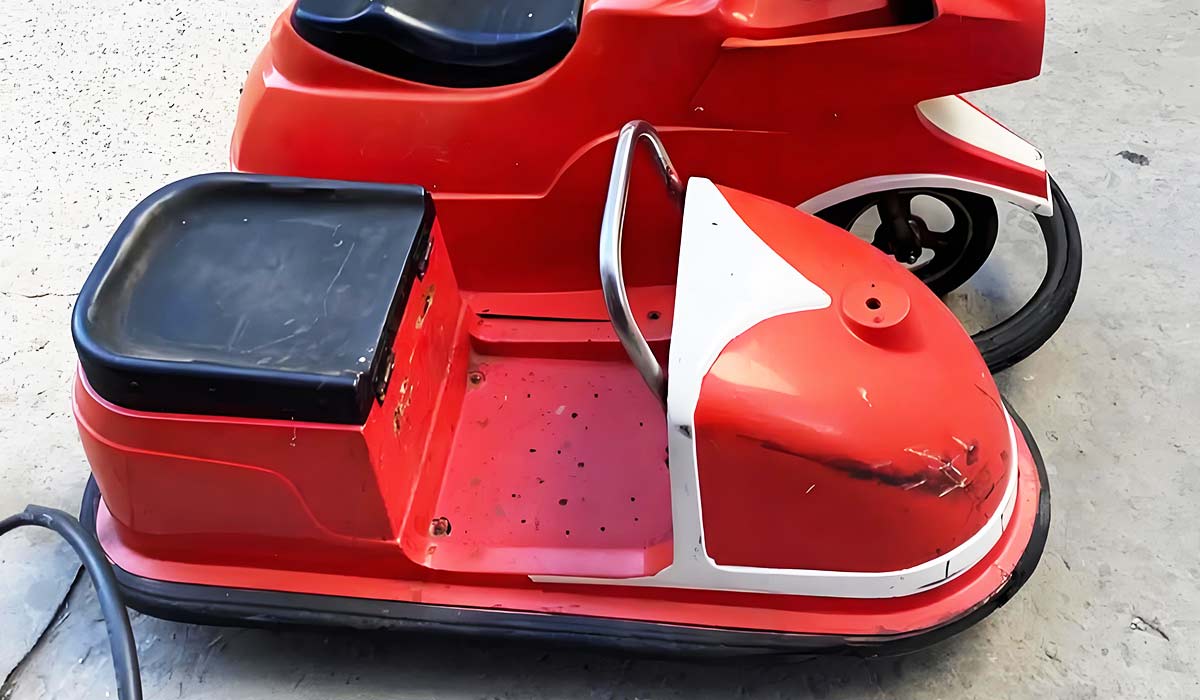

In the 1960s, trackless bumper cars were introduced, which allowed for even more freedom of movement. Instead of being limited to a track, these cars could move freely around the arena, giving riders a more immersive experience. Modern bumper cars have continued to evolve, using innovations like LED lighting, battery-powered systems, and even interactive features like digital scoring.
Today, bumper cars are not just for children—they’re a thrilling experience for people of all ages. From mini dodgem cars designed for younger riders to larger, faster cars for adults, bumper cars are a versatile and fun ride that adapts to the needs of the entire family.
Names and Variations: Known as dodgems in the UK, bumper cars are also referred to as auto-skooters and bumpeez in different countries.
Pop Culture: Bumper cars have appeared in numerous films and TV shows, becoming cultural icons.
Record-Breaking Rides: In 2012, Martin Rees set the world record for the longest bumper car marathon, driving for 26 hours straight.
Competitive Events: Some places even host bumper car competitions, where participants race to score points or navigate obstacles.
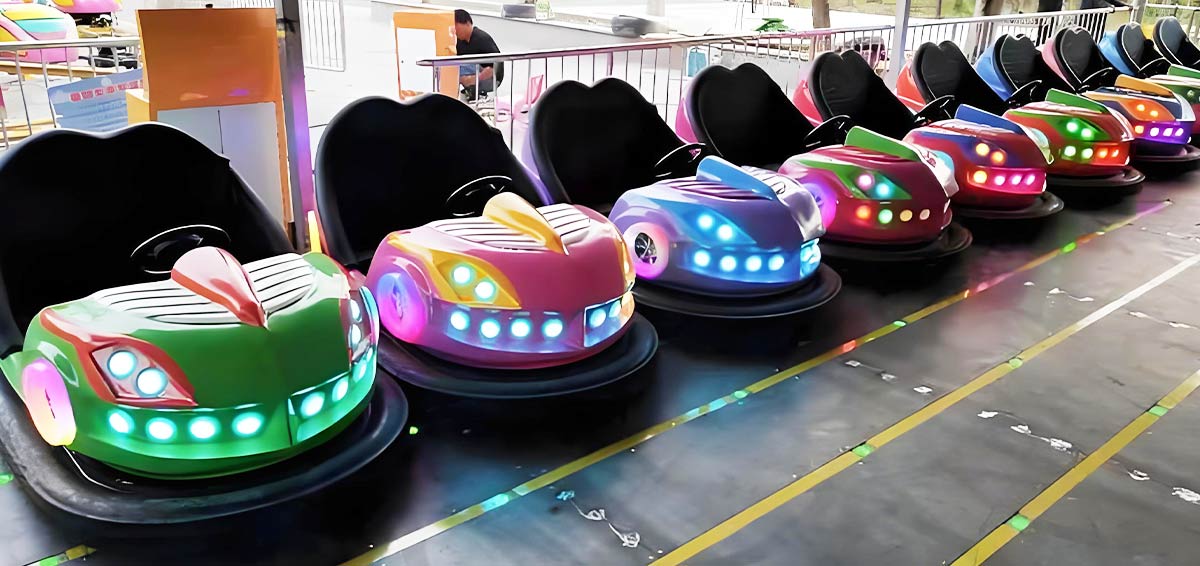

Even in an age of high-tech roller coasters and VR experiences, bumper cars remain one of the most beloved and enduring rides at amusement parks around the world. The sheer joy of driving a small car, crashing into others, and feeling the impact without real consequences is a thrill that appeals to all ages.
Whether you're dodging your friends or trying to bump your way to victory, bumper cars offer a unique form of entertainment that no other ride quite matches. The blend of fun, physicality, and nostalgia makes them a timeless attraction.
Bumper cars have come a long way since their early days of tin and unreliable steering. From dodgem cars to modern battery-powered models, these fun, safe, and exhilarating rides continue to delight millions of people around the world. If you're looking to add a bumper car experience to your event, whether it's a wedding, corporate gathering, or a fun park attraction, you can easily find bumper cars for sale online and bring the thrill to your own venue.
So next time you buckle up for a dodgem ride, remember you’re part of a century-old tradition that continues to bring joy to families everywhere. Whether you’re in a mini dodgem car or a full-sized dodgem bumper car, the ride will never lose its magic.
1. Introduction to Bumper Cars: History, Function, and Fun Facts for the Whole Family
2. Bumper Car History: 7 Facts About Dodgems You Never Knew
Please contact us for free quotation by form below. We promise the quickest response within 24 hours: